Visit the College Board on the Web. The angular acyereration of the pulley ii.

Spin Disk Solid Physics High School Physics Disk
Place the object on the disk and measure the distance from the center of the disk to the center of mass of the object by using a meterstick.

. See Science Practices 12 14 LO 5D31. The release of oxygen. The disk shown above spins about the axle at its center.
Object A initially moves to the right with speed 300 so that it collides with object B. At the bottom of the incline the center of mass of the cylinder has a translational speed of 50 ms. A box slides down an adjacent frictionless incline of the same height.
This was my original solution which came out incorrect a friend then told me that τ4 is zero because the force of 20N is not being applied to a point on the disk itself so then. A The object will be moving eastward when the force drops to zero newtons. Place the green plant leaves in a bowl and cover the bowl with aluminum foil.
A horizontal disk of radius 02 m and mass 03 kg is mounted on a central vertical axle so that a student can study the relationship between net torque and change in angular momentum of the disk. In terms of M R and g determine each of the following. Express your-answers to the following in terms of M and vo a Determine the total momentum of the system of the two objects.
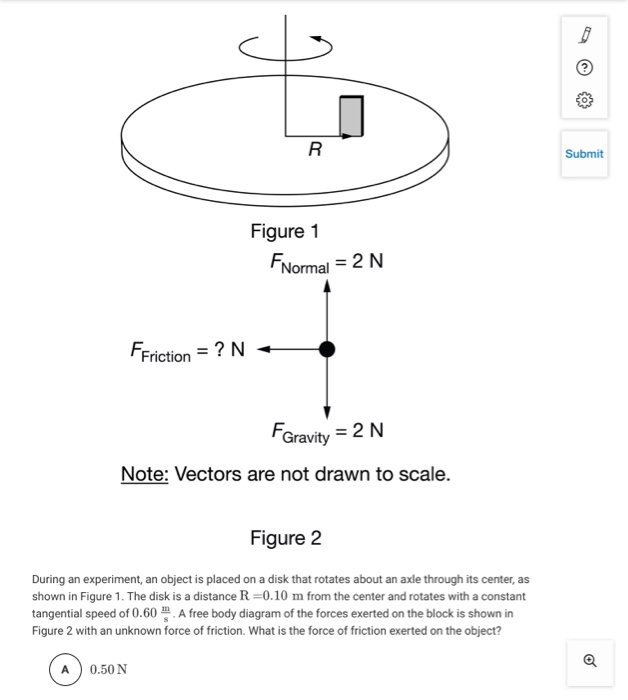
If the disk has an angular acceleration the object has both a centripetal and a tangential acceleration. During an experiment a block of mass M020kgM020kg is placed on a disk that rotates about an axle through its center as shown in the diagram. Figure 2 During an experiment an object is placed on a disk that rotates about an axle through its center as shown in Figure 1.
Consider an object on a rotating disk a distance r from its center held in place on the disk by static friction. Which of the following procedures could be used to make the necessary measurements to find the coefficient of static friction between the object and the disk. During an experiment an object is placed on a disk that rotates about an axle through its center as shown in Figure 1.
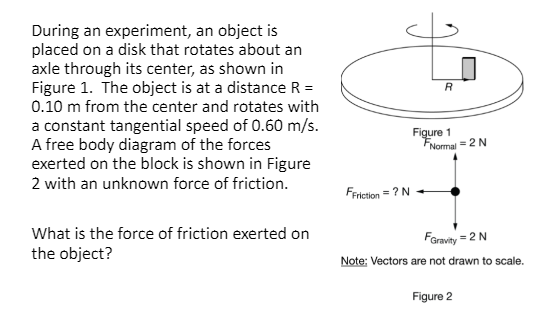
Store the bowl in a cool place to keep the leaves fresh until you use them. If the angular speed is constant the object is not. The disk is a distance R010 m from the center and rotates with a constant tangential speed of 060 A free body diagram of the forces exerted on the block is shown in Figure 2 with an unknown force of friction.
During an experiment an object is placed on a disk that rotates about an axle through its center as shown in Figure 1. Demonstration of Release of Oxygen during Photosynthesis. The disk is a distance R 010 m from the center and rotates with a constant tangential speed of 060 ms.
Try not to create too many bubbles. Record the time in which the object makes one revolution around the center of the disk. Slowly increase the rate the disk rotates until the object begins to slide off the disk.
A students experiments reveal that while the disk is spinning friction between the axle and the disk exerts a constant torque on the disk. A portion of the recorded data is shown in the figure above. The block is moved to different distances R from the axle and the tangential speed of the block is gradually increased until the mass begins to slip.
On the diagram below draw and identify all of the forces acting on the pulley and on the block. During an experiment a block of mass M020kg is placed on a disk that rotates about an axle through its center as shown in the diagram. An experiment is performed in a physics class where three objects an empty can a D battery and a marble roll down an incline of height H without slipping.
Situation in which angular momentum changes due to interaction with other objects or systems. The torque on the pulley iii. C The direction of the objects acceleration depends on how fast the object was initially moving.
Which of the following statements is not true concerning this object. The tension in the cord ii. Measure Photosynthesis with Floating Leaves.
Here is a list of top ten experiments on photosynthesis with diagram. τ1 30N 01 sin90. B The change in the velocity of the object is directed north of west.
Slowly increase the rate the disk rotates until the object begins to slide off the disk. Few branches of an aquatic plant ie Hydrilia etc beaker glass funnel test tube sodium bicarbonate etc. Disk m B R 1 2 v B 2gh 1 I disk m B R 1 2 47 ms 13.
Which of the four objects reaches the bottom of their inclined planes first. How far does the cylinder travel up along the path of the incline. A solid cylinder of mass 10 kg rolls up an incline at an angle of 30.
The amount of time it takes the object to make one revolution around the center of the circle may be set at a known value. The object is at a distance R 010 m from the center and rotates with a constant tangential speed of 060 ms. B A student predicts that the collision will be totally inelastic the objects stick together on collision.
Record the time in which the object makes one revolution around the center of the disk. The block is moved to different distances RR from the axle and the tangential speed of the block is. The student is able to predict the velocity of the center of mass of a system when there is no interaction outside of the system but there is an interaction within the system ie the student simply.
A student sets an object attached to a spring into oscillatory motion and uses a motion detector to record the velocity of the object as a function of time. A free body diagram of the forces exerted on the block is shown in Figure 2 with an unknown force of friction. Up to 24 cash back measured to be 23g in an experiment using a computer-controlled motion sensor.
In the experiment the student uses a force probe to collect data pertaining to the net torque exerted on the edge of the disk as a function of time as shown in the graph. The total change in the objects speed between 10 s and 11 s is most nearly. Place the object on the disk and measure the distance from the center of the disk to the center of mass of the object by using a meterstick.
Watch the Leaf Disk Assay video to familiarize yourself with the procedure. An object is placed on a rotating disk.

Figure A Shows Three Incident Rays 1 2 And 3 Falling On A Convex Mirror Ray 1 Falls Parallel Ray 2 Falls Making An Angle With Physics Mirror Refraction

Solved Submit Figure 1 Fnormal 2 N Ffriction N Chegg Com
0 Comments